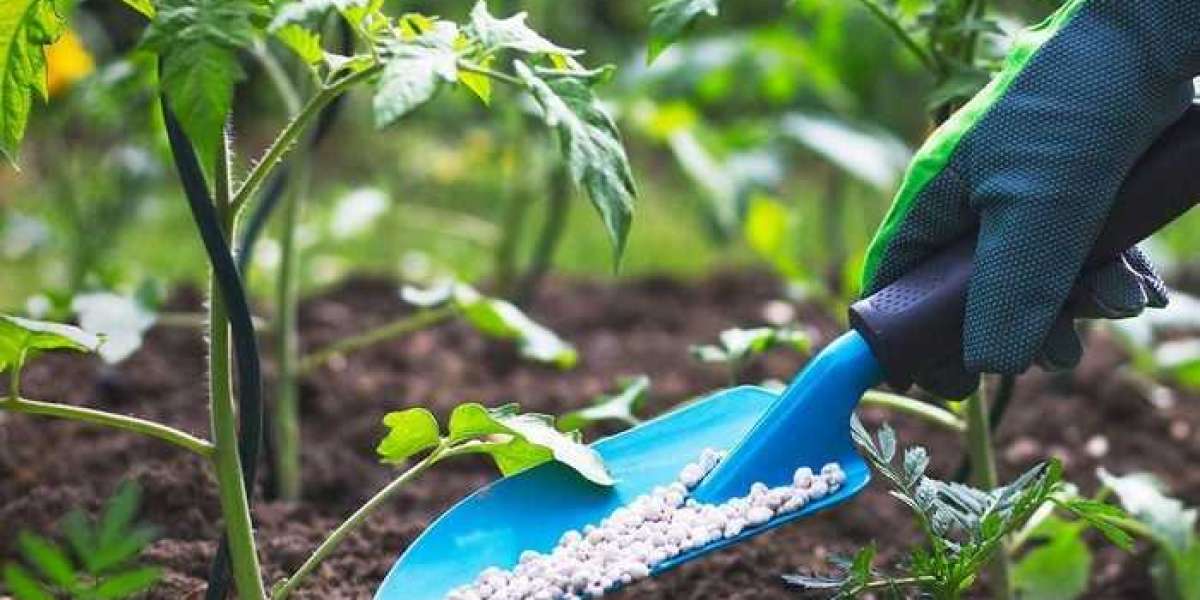
Understand Your Plants' Needs:
Different plants have different nutritional requirements. Before selecting a plant fertilizer, identify the specific needs of your plants. Some plants may require a balanced fertilizer, while others might need more nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium.
NPK Ratio:
Plant Fertilizers contain three primary nutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K), represented by the NPK ratio on the packaging. Choose a fertilizer with an NPK ratio that matches your plants' growth stage. For instance, a balanced ratio like 10-10-10 is suitable for overall growth, while a higher phosphorus content (e.g., 5-10-5) is beneficial for flowering and fruiting plants.
Slow-Release vs. Quick-Release:
Fertilizers come in slow-release and quick-release forms. Slow-release Plant fertilizers provide nutrients gradually over an extended period, promoting sustained growth. Quick-release fertilizers provide a rapid nutrient boost but may require more frequent applications. Choose based on your gardening preferences and the specific needs of your plants.
Organic vs. Synthetic:
Decide whether you prefer organic or synthetic Plant fertilizers. Organic options, such as compost, manure, and fish emulsion, contribute to soil health and microbial activity. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, offer precise nutrient content and are quickly absorbed by plants. Consider factors like your gardening philosophy, environmental impact, and the specific requirements of your plants.
Micronutrients:
In addition to the primary nutrients (N, P, K), plants also require micronutrients like iron, magnesium, and zinc. Some Plant fertilizers include these micronutrients, while others may require supplemental applications. Ensure your chosen fertilizer provides a well-rounded nutrient profile to prevent deficiencies.
Soil Test:
Conduct a soil test to determine the existing nutrient levels in your soil. This will help you identify any deficiencies and tailor your fertilizer choice accordingly. Many local agricultural extension offices or garden centers offer soil testing services.
Water-Soluble vs. Granular:
Fertilizers come in water-soluble and granular forms. Water-soluble plant fertilizers are mixed with water and applied directly to the soil or foliage. Granular fertilizers are applied to the soil surface and release nutrients over time. Choose the form that aligns with your preferred method of application and the needs of your plants.
Seasonal Adjustments:
Consider seasonal changes when selecting plant fertilizer. Plants may have different nutrient requirements during various stages of growth or in different seasons. Adjust your fertilizer regimen accordingly to provide optimal nutrition throughout the year.
Brand Reputation and Reviews:
Research and choose reputable plant fertilizer brands. Read reviews from other gardeners to gauge the effectiveness and satisfaction of users with a particular product.
By considering these factors, you can choose a plant fertilizer that suits your gardening goals and ensures the health and vitality of your plants.